China-Pakistan Thematic Webinar on Natural Disaster and Risk Management

July 22nd, 2021 11:00-14:00 (Pakistan Standard Time)
14:00-17:00 (Beijing Time)
Meeting Platform: Voov Meeting
ID: 554 373 550
Live Streaming:

Organizers
I. Background and Objective
In today’s world, with ever-increasing globalization, the escalating competition and cooperation among countries and regions in energy, resources, sciences, technologies and economy, etc. are growing constantly. The establishment of China-Pakistan Joint Research Centre on Earth Sciences (hereinafter referred to as CPJRC) will play a critical role in promoting academic and scientific exchange and collaboration between Pakistan and China. In the past few decades, Pakistan has experienced dozens of geological disasters, including earthquakes, landslides, debris flow, floods, droughts, etc. The magnitude 7.6 earthquake in Muzaffarabad in 2005 caused 83,000 deaths and damages to 2.5 million people. The super flood in 2010 affected daily life of 20 million people and left 2,000 people dead in Pakistan. How to effectively and scientifically respond to extraordinary natural disasters has become a huge challenge facing the construction of China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, hence a main academic purpose of CPJRC.
The thematic webinar will focus on the scientific research goals of the field of natural hazards of CPJRC, review the relevant research work and scientific research results achieved in the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor by various research directions in recent years, propose natural disaster risk countermeasures, and serve the sustainable development of the region.
I. Agenda (Pakistan Standard Time)
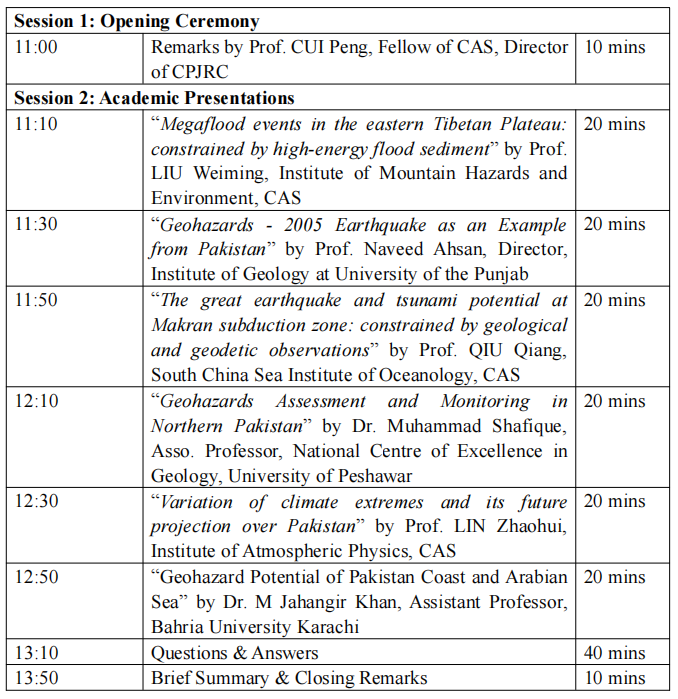
II. Organizer & Sponsor
China-Pakistan Joint Research Centre on Earth Sciences
Partner Organizations
|
Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, CAS |
|
Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration |
|
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, CAS |
|
Institute of Earth Environment, CAS |
|
Institute of Geology and Geophysics, CAS |
|
South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, CAS |
