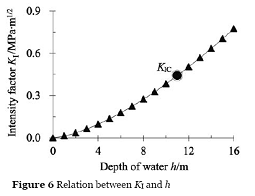
Rainfall is one of the important factors that trigger postearthquake bedrock landslides. However, the mechanism of its effects on the failure of rock landslides is not clear because of the slope variation. Therefore, Prof WU Yong, HE Siming and their team from Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, CAS, take a typical post-earthquake bedrock landslide with a translation sliding surface in Yingxiu section of the Dujiangyan-Wenchuan highway as an example and analyze quantitatively the effects of water infiltrated into fractures on the stability of rock slopes ,base on the viewpoint of fracture mechanics, post-earthquake conditions, the mechanisms of crack propagation, water infiltration and development of the sliding surface. The research results show that the propagation and coalescence of cracks and the lubrication of incipient sliding surfaces are the main causes of the failure of post-earthquake rock landslides in response to rainfall.


WU Yong, HE Siming, LUO Yu, LI Xinpo. Failure Mechanisms of Post-Earthquake Bedrock Landslides in Response to Rainfall Infiltration. Journal of Mountain Science, (2011) 8:96-102
. (Download Here: http://www.springerlink.com/content/gw22472467064626/)
